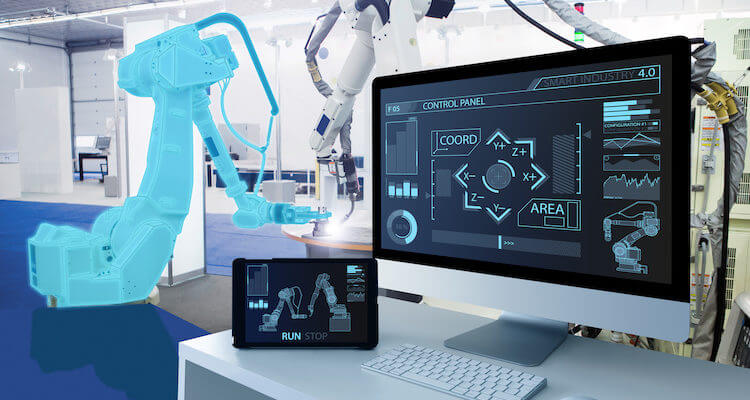
What is a Human-Machine Interface (HMI)?
A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is a digital device designed for interaction with industrial control systems such as PLCs, inverters, and controllers. It includes both hardware and software components, allowing operators to input commands and monitor machine parameters via screens and input devices like touchscreens, keyboards, and mice.
Industrial Benefits of HMIs
- Efficient Maintenance and Monitoring:
HMIs offer real-time data visualization and diagnostics when connected to PLCs. This reduces the need for frequent laptop or computer connections, saving time and improving maintenance efficiency. - Centralized Control for Multiple Devices:
Modern HMIs allow operators to monitor and control multiple systems from a central location, benefiting large plants by providing centralized control. - Remote Monitoring for Critical Systems:
For facilities like water treatment plants, HMIs enable remote monitoring and control of equipment, ensuring continuous operation and minimizing downtime.

How HMI Connects to Machines
Programming and Interfacing:
Engineers use specialized software to program HMIs, designing screens with data displays and control buttons. The software ensures that the HMI can display data such as tank levels or provide control over machinery like pumps.
Interaction Between HMI and PLC:
HMIs interact with PLCs through industrial communication protocols like Modbus, Ethernet/IP, or Profibus. This facilitates seamless data exchange, allowing for efficient control and monitoring.
Key Functions of HMI Products
Device Monitoring and Control:
HMIs offer real-time monitoring of machine states with visual indicators, enabling operators to input data and control machinery, such as starting or stopping it.
Data Logging and Recipe Management:
HMIs can store and manage production data, enhancing process consistency and traceability by allowing easy access to production parameters and recipes.
Basic Logic and Calculations:
HMIs can perform simple logic and numerical calculations, enabling basic control decisions to be made directly through the interface, reducing PLC programming complexity.
Connectivity to Various Industrial Devices:
HMIs connect to a range of industrial systems, making them essential in modern industrial environments due to their versatility and integration capabilities.

Types of HMI Products
- Basic HMI Products:
These smaller devices feature membrane key-input systems with screens under 5.7 inches. They are commonly used in simple, smaller applications. - Mid-range HMI Products:
Mid-range HMIs with 5.7 to 12.1-inch touchscreens are versatile and come with advanced features, often using free screen configuration software. - High-end HMI Products:
High-end systems, often larger than 10.4 inches, are tablet-based and provide advanced features like multiple communication ports, making them suitable for complex industrial applications.
How Siemens HMI Communicates with PLC
- Integrated Connection Method:
In this method, the PLC and HMI are part of the same project, allowing direct access to PLC variables through the HMI variable table for seamless integration. - Non-integrated Connection Method:
In this setup, the PLC and HMI are separate projects. The HMI’s communication list establishes connections, using absolute addressing to link PLC variables.